Learn how to optimize your site for search engines (SEO)

SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is all about getting free traffic from search engines. It involves fine-tuning your website to rank higher in search results pages (SERPs). The higher your website ranks, the more people will see it, naturally leading to more visitors.
This approach is similar to building a strong foundation. Just like Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs prioritizes basic needs before reaching for higher-level goals, effective SEO starts with core optimization techniques before tackling more advanced strategies.

What are the three pillars of SEO?
Mastering SEO is crucial for digital marketers. It ensures your website gets discovered by potential customers. While SEO adapts over time, its core stays the same. Here are the three pillars you need to understand and implement:
- Technical SEO: This is the groundwork. It involves optimizing the technical aspects of your website to make it search engine friendly. Think of it as building a solid foundation for your house. Submitting your sitemap to Google is a technical SEO task.
On-Page SEO: This focuses on the content itself. It involves creating relevant and informative content that users will enjoy. Here, you target the right keywords within your content, ensuring it aligns with search queries. Most Content Management Systems (CMS) like WordPress or Wix allow for on-page optimization.
Off-Page SEO: This involves building your website’s reputation outside your own site. Earning high-quality backlinks from other websites is key here. Backlinks act like recommendations, boosting your site’s credibility in the eyes of search engines.
By focusing on these three pillars, you can improve your website’s ranking and attract more organic traffic.
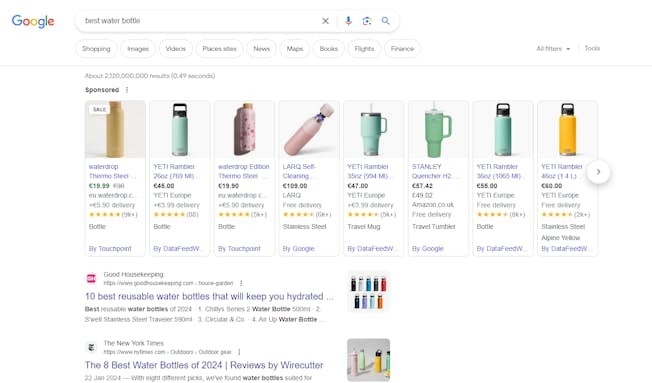
Head-to-Head: Paid Search vs. Organic Search
Before diving into SEO, it’s crucial to grasp the differences between organic search and paid search. Both aim to get your website seen, but they work in distinct ways.
- Position in Search Results: Paid ads take the top spots, often marked as “Sponsored” or “Ads.” Organic results appear below them. Think of paid ads as prime real estate, grabbing immediate attention.
- Time to Results: Paid search delivers instant visibility. You can see your ad appear as soon as your campaign launches. Organic search takes time and effort. It can take weeks, months, or even years to climb the search rankings for competitive keywords.
- Cost: Paid search requires ongoing investment. You pay a fee (usually per click) each time someone clicks on your ad. Organic search is free in terms of direct cost, but it requires time and resources to optimize your website.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Measuring ROI is easier with paid search. You have access to detailed keyword data, making it clear what’s working and what’s not. However, ROI can decline over time as competition grows. Organic search ROI takes longer to see, but it can be highly rewarding in the long run. As your website climbs the rankings, you can enjoy a steady stream of free traffic.
Behind the Scenes: How Search Engines Find Your Answers
Ever wondered how you get the perfect answer to your online questions? That’s the magic of search engines! But how do they work?
Search engines rely on clever programs called algorithms. These algorithms act like tireless detectives, scouring the web for relevant information. They consider various clues to understand what each webpage is about and how well it matches your search query.
Social media algorithms work differently, focusing on curating content specific to your interests within those platforms.
Step 1: Crawling the Web – Like a Spider on the Hunt
Imagine millions of tiny explorers venturing out into the vast digital world. These are search engine crawlers, sometimes called spiders or robots. Their mission? To discover new web pages and keep track of existing ones.
Crawlers follow links like breadcrumbs, starting from known websites and hopping to new pages they discover. They also revisit previously crawled pages to catch any updates or changes.
Step 2: Indexing – The Search Engine’s Library
Not every webpage makes the cut. Indexing is like a search engine’s library, where only valuable and relevant content gets stored. Here’s what can prevent a page from being indexed:
Duplicate content: If the information is already present elsewhere, it might not be added again.
Low-quality content: Spammy or thin content with little value gets left behind.
Crawling issues: If crawlers can’t access the page or encounter technical problems, it can be excluded.
Lack of credibility: Websites without many reputable links pointing to them might be seen as less trustworthy.
Step 3: Ranking – The Moment of Truth
This is where the magic happens! Ranking is when search engines decide which webpages deserve the top spots for a particular search query. But ranking only occurs after crawling and indexing.
Search engines consider hundreds of ranking signals, all of which fall under three main categories, known as the three pillars of SEO:
Technical SEO: This ensures your website is built in a way search engines can easily understand and navigate. Think of it as building a house with a solid foundation. A fast loading speed and mobile-friendliness are examples of technical SEO factors.
On-Page SEO: This focuses on the content itself. Does your content include relevant keywords and provide valuable information for users? Does your title tag accurately reflect the content’s topic? These are all aspects of on-page SEO.
Off-Page SEO: This involves building your website’s reputation outside your own site. The more high-quality backlinks (links from other websites) pointing to your page, the more trustworthy it appears to search engines.
In this article, we discussed the function and importance of SEO in the digital world. If you are interested, you can learn more about digital marketing and Google advertising by viewing other articles on the Kayoads website.